A Coccidian Parasite Inhabiting the GI Tract and Leucocytes of Styela plicata (Lesuaer, 1823) and Ciona intestinalis (Linnaeus, 1767) Sampled from the Arabian Gulf (Saudi Arabia) 
2. Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt
 Author
Author  Correspondence author
Correspondence author
International Journal of Marine Science, 2016, Vol. 6, No. 18 doi: 10.5376/ijms.2016.06.0018
Received: 29 Feb., 2016 Accepted: 26 Apr., 2016 Published: 26 Apr., 2016
Saad G.A., 2016, A Coccidian Parasite Inhabiting The GI Tract and Leucocytes of Styela plicata (Lesuaer, 1823) and Ciona intestinalis (Linnaeus, 1767) Sampled from the Arabian Gulf (Saudi Arabia), International Journal of Marine Science, 6(18): 1-14 (doi:10.5376/ijms.2016.06.0018)
Styela plicata and Ciona intestinalis were collected from the shallow water of the Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia during 2011 – 2014. Breeding and non breeding seasons were considered. Specimens were dissected alive in seawater and isolated parts from the intestine were sampled. In a previous study, a sporocyst of a coccidian was observed completely embedded in the intestinal epithelial cells of Styela plicata. Since that time, the author tried to find all stages of the life cycle of this coccidian parasite and describe them. Ascidians may obtain parasites from their food through water filtration, or directly swallow an unsporulated oocyst with incurrent water. Sporozoites initiate infection probably homoxenously or heteroxenously. Sporozoites then enter host intestinal epithelial cells and there transform into meronts. Merozoites of the final merogony enter blood cells to initiate the gametic cycle, and become either macrogamonts or microgamonts. Microgamontes became trophozoites (uninucleated zoite). These divide by multiple fission to produce large numbers of flagellated microgametes. Macrogamonts develop into macrogametes without further division. Syngamy produces zygotes, then merogony proceeds to form merozoites which enter new host cells extraintestinal like blood cells to produce more merogonous cycles. The present study concluded that the investigated parasite may belong to Genus Isospora (schneider, 1881). Since in isosporans sporogony leads to the formation of four sporozoites inside each sporoblast and this agametic phase develop extraintestinal.
Introduction
The pathogens of interest are those commonly associated with diseases. In many marine organisms health assessments, the role of parasites on their hygiene can be overlooked. Their presence is usually only a concern when they affect an edible species of interest, or cause detrimental effects to the economy or a recreational activity, or a commercial fishery. Parasitic species can be found everywhere, and on every living organism. Their presence in their host is generally at equilibrium in marine organisms and the most common lifestyle on the planet (Marcogliese, 2005). Consequently, it is difficult to find any environment or organism that can be labeled as ‘pristine’ or parasite-free. When researchers describe control sites as being pristine, pathogen or disease-free, they are merely describing the lack of viruses, bacteria and xenobiotics, and are not generally referring to parasites. There are times when changes in the environment (natural or anthropogenic) can change the state of balance of the parasite between host and nature, thus resulting in disease. These changes can be environmental such as temperature, climate, or anthropogenic such as pollution and urbanization (Lafferty and Kuris, 1999). When the dynamic equilibrium between host and parasite is lost, some changes can occur within the host. These changes can cause mechanical damage (fusion of gill lamellae, tissue replacement), physiological damage (cell proliferation, immunomodulation, altered growth, detrimental behavioral responses,) and/or reproductive damage (Buchman and Lindstrّm, 2002, Knudsen et al., 2009; Diouf and Toguebaye, 2013). The roles, functions, and life-styles of parasites help to characterize an ecosystem. Knowledge of parasites and parasitic communities, allows researchers to recognize the role of the marine organism`s host in the food web or ecosystem (Marcogliese and Cone, 1997; Overstreet, 1997; Marcogliese, 2005), determine changes in host diet (Campbell et al., 1980; Huxham et al., 1995; Pascual et al., 1996; Knudsen et al., 2004), relationships of host with other organisms (Marcogliese, 2005), describe niche changes (Marcogliese, 2005), determine the presence of predators or seasonal migrants (George-Nascimento, 1987; Jirku et al., 2002), and determine changes from pollution and climatic stressors (Overstreet, 1981, 1993; Overstreet, et al., 1984, Khan and Thulin, 1991, Mackenzie et al., 1995; Marcogleise, 2004; Jirku and Modry, 2006; Duszynski et al., 2007). This overview is meant to provide a deeper appreciation for the role of parasites in marine organism`s health assessments.
The general lack of information on ascidian parasites applies equally to the protozoa and helminthes. Although behavior, ecology and physiology are well known, relatively few studies have documented the incidence of parasites and their influence on their hosts (Hoberg 1996, Upton, 2000). Many ascidians, including Styela plicata, Styela partita and Ascidia mentula breed during summer in Mediterranean Sea (Saad, 2008, 2010). Ascidians serve as ideal habitats for ectoparasites (own observation; Cox, 1994). Many parasitic species have become highly specialized in synchronizing their life cycles with their hosts’ breeding phenology (Marcogliese, 2004). However, most species of ascidians spend the greater part of the year in dispersed estuaries like Arabian Gulf where transmission and survival of parasites represents a major challenge. Nevertheless, foraging behavior and diet facilitate the transmission of a variety of endoparasites through marine invertebrate and vertebrate species. Ciancio et al., (1999) studied the vegetative and sporulation stages of Hapiosporidium ascidiarum from the ascidian Ciona intestinaiis. Scippa et al., (2000) observed an Apicomplexan microparasite from the Pericardic Body of Ciona intestinalis. Although those parasites, too, are better transmitted during the breeding season because of the abundance of marine littoral intermediate hosts (Hoberg, 1996). The colonial ascidian Botryllus schlosseri is a stable microhabitat potentially favourable for feeding, shelter, brooding and reproduction of many marine microorganisms. Saad and Barakat (2010) identified the microfauna including parasites living on and in this colonial ascidian using light and electron microscopies.
Ascidians may obtain microorganisms or/and parasites from their food through water filtration, or directly swallow an unsporulated parasitic stage in the sea water. Parasites may have complex life-cycles involving up to 3 or more different host species (including ascidians), or direct life-cycles involving a single host species. Ascidians are probably infected when they ingest infected crustaceans.
I found accidently in a previous study a coccidian sporocyst completely embedded in the intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata (Saad, 2008). Later on I tried to find and collect all stages of the life cycle of this coccidian parasite. This study based totally on natural infection in the marine ecosystem and continued four years.
Materials and Methods
Adult specimens of Styela plicata (Lesuaer, 1823) and Ciona intestinalis (Linnaeus, 1767) were collected from the shallow waters of the Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia during 2011 – 2014. Breeding and non breeding seasons were considered according to Saad, 2008, 2010; Saad, et al., 2011). Identification of these ascidians was carried out according to Millar (1988).
Microscopic observation
Adult specimens were dissected alive in seawater and isolated parts from the gastrointestinal tract were fixed in 10% formalin and washed in distilled water for 24 hours. Ascending series of ethyl alcohol used for dehydration, followed by another dehydration series of tertiary butyl alcohol, then tertiary butanol and paraffin oil (1:1) and finally in pure paraffin oil. All preparations were washed in tissue mate (paraplast) with melting point 54-58°C and blocked in fresh paraplast. Sections of 5-8µm were obtained. A number of triple stains were tried to enable the differentiation of the tissues (Toluidine Blue Pearse, 1968; Mercury bromphenol blue Pantin, 1948). Ortholux Leintz Wetzler Stereoscopic microscope with different magnification capacities and Lampe house 250 with external light source of Schott KL 1500 was used. The Camera used was full-automatic microscope camera for research and laboratory purposes.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
Parts from the intestine of Styela plicata and Ciona intestinalis were fixed in PAF (picric acid-formaldehyde) 1200 mOsm pH 7.5. These parts were dehydrated in a graded ethanol series. The dehydrated larvae were critical point dried, mounted on specimen holders, and subsequently sputter-coated with gold. Specimens were examined and photographed using a FEI Quanta 200 SEM at 15 kV.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
Parts from the intestine of Styela plicata and Ciona intestinalis were fixed in 2.5% Glutaraldehyde in 0.05 M PBS containing 0.33 M NaCl (1 h, 4°C). The fixative was removed by washing specimens several times with PBS. Post-fixation was carried out using 2% Osmium tetroxide in PBS for 30-60 min at 4°C. Specimens were subsequently washed with PBS, dehydrated in a graded ethanol series, and propylene oxide and embedded in araldite resin. Ultrathin (60-70 nm) sections were obtained using Leica UC6 microtome equipped with diamond knives. Ultrathin sections were picked with formvar-coated singleslot copper grids, stained automatically with uranyl acetate and lead citrate in a Nanofilm TEM STAINER, and examined on a Phillips CM 120 transmission electron microscope at 60 kV.
Results
Styela plicata (Fig.1) can be differentiated from other neighbouring ascidians as follows: the size ranges10-90 mm in length and 40-50 mm in width, siphons (oral or atrial) are quadrilobed, the later siphon is subterminal, stigmata straight, oral tentacles are simple, four pairs of branchial folds, dorsal lamina is continuous, stomach without hepatic diverticula and gonads are 4 in the right side and 1 or maximally 2 in the left side. Ciona intestinalis (Fig.2) was brownish-white coloured and transparent to the extent that one can see the internal viscera while alive. It is large-sized measuring about 40-100 mm in length and 20-35 mm in width. The body is cylindrical, longitudinal muscles of branchial basket are conspicuous, oral siphon is terminal with 8 lobes and red or orange pigment spots between lobes, atrial siphon is subterminal with 6 lobes and pigment spots, stigmata straight, stomach and intestinal loop behind branchial sac, longitudinal branchial bars are papillated, ovary is compact and situated in the intestinal loop whereas testis diffusely spread over stomach and intestine.
The gastrointestinal tract of solitary ascidians begins with the oral opening which lies at the base of oral siphon and leads to an immense pharynx. This chamber serves both respiration and filter feeding. The pharynx is perforated by dorsoventral rows of numerous gill slits called stigmata. Blood vessels traverse the pharyngeal wall between the slits. Water passes through the gill slits to the atrium and then is expelled through the atrial opening. Along the ventral margin of the branchial basket is a specialized organ called endostyle. The endostyle secretes large quantities of mucus which is distributed as a thin sheet over the inner surface of the pharynx by the flagella and pharyngeal cilia. Food particles become entangled in the mucus, are collected along the dorsal wall of the pharynx and are propelled by ciliary action to the oesophagus behind the pharynx. The digestive tract leads to a stomach at the bottom of the U-shaped digestive loop and an intestine terminates at the anus which opens in the atrial cavity.
Artificial infection of the ascidian with parasite did not carried out because of difficulties into rearing ascidians for a long time. This work lasted about four years.
Gametic cycle of the coccidian parasite
Gamonts were observed while spreading along the intestinal epithelial cells inside white blood cells of an infected of Ciona intestinalis.
Merozoites were released from the gamonts after complete destruction of the host intestinal epithelial cell. They wandered freely in the circulatory system and penetrated new host blood cells (Figs.3-8). Merozoites later transformed from the cylindre banana motile form to spherical form and lost characters from its apical complex represented by micronemes, rhoptries and polar ring. Early formed gamonts were surrounded by parasitophorous vacuole which was spherical in shape and began small sized (5.5 X 3.8 µm). Gamonts later differentiate to macro- and microgamonts (Figs.3-8). The macrogamonts (6 X 5.6 µm) were provided with large nuclei and prominent nucleoli. Finally macrogamont transformed into macrogametes without further division and provided with small dense granules and large amylopectin granules in the cytoplasm (Fig.8). The parasitophorous vacuole became narrow as the parasite increased in size or in other cases tear off due to parasite`s huge-size (Fig.7). Microgamonts underwent multiple fission and spread along the intestinal epithelia (Figs.3-8). More than one microgamont can be seen inside blood cells in one epithelial cell (Fig.7). Microgamonts grew after penetration of merozoites to the blood cells and became a uninucleated zoite (Fig.8). The later grew in size to reach 4.6 X 4.5 µm and the parasitophorous vacuole enlarges too. The nucleus of the uninucleated zoite underwent many divisions (Fig.3). Later the microgamont had a large lobulated nucleus. This suggests that the nucleus underwent endopolygony. The lobules of the nucleus began to separate and migrated to the external of the microgamont. Microgametes appeared as evaginations of the external boundary of the microgamont inside the parasitophorous vacuole (Fig.8). As development proceeded, the flagellated microgametes were released and left the rest of the cytoplasm inside the microgamont (Figs.9-11).
Syngamy took place and the spherical zygote with centrally located nucleus was formed (11.1 X 8.3 µm). As an external wall gradually formed, the zygote transformed into an oocyst (Fig.12) with two types of granules in the cytoplasm, amylopectins and small sized lipid granules.
As sporogony proceeded, the oocyst shrank (4.8 X 5 µm) and its wall thickened. The micropyle with its cap were out of focus. The nucleus of the completely formed oocyst (Figs.13–14) (13.8 X 10.1 µm) began to divide into two nuclei followed by cytokinesis forming two sporoblasts, later on the nucleus of each sporoblast divided into four small nuclei, the later surrounded with a part of cytoplasm and formed four sporozoites (Fig.14). In this way eight sporozoites would form from the two sporoblasts leaving residual cytoplasm (Figs.13-15). This study concluded that the macrogamonts, the zygote and the oocyst are formed extraintestinal inside blood cells. This study observed the later stages inside leucocytes.
Ultrastructurally, uninucleated zoites were observed in leucocytes but it was very difficult to determine whether this stage was also extracellular (Fig.16). This stage had a large prominent nucleus with only mitochondria in its cytoplasm, dense granules and microtubules (Fig.17). This stage became gradually irregular in shape. Remains of micronemes were observed adhering to the pellicle interiorly as if it secretes its contents inside the parasitiphorous vacuole. Fully formed gamonts appeared without apical complexes, each surrounded by a vacuole with thin wall and filled with electron dense compact material. Gamonts enlarged in diameter and the contents of their vacuoles disappeared except some microtubules. The wall of each vacuole differentiated into an outer dense electron layer and an inner light electron one. The fully formed gamont appeared irregular with an irregularly-shaped nucleus, ER and a number of vacuoles containing filamentous structures (Figs.18-19). Microgamonts were spherical in shape with prominent nuclei and peripherally situated chromatin. It contained a number of microtubules underneath its pellicle, a number of mitochondria in the cytoplasm and the parasitophorous vacuole appeared later (Fig.19). Bodies with dense electron material appeared in the zygote similar to that of wall forming bodies. Smaller bodies with dense electron material were observed perhaps they represent the wall forming bodies (Figs.20 -21).
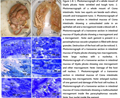 Figure 1-8 1. Photomacrograph of a whole mount of Styela plicata. Note: wrinkled and tough tunic. 2. Photomacrograph of a whole mount of Ciona intestinalis. Note: two squirts are beside each others; smooth and transparent tunic. 3. Photomicrograph of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Ciona intestinalis showing a uninucleated zoite in an epithelial cell and a microgamont inside a blood cell. 4. Photomicrograph of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata showing a macrogamont and a microgamont . Note: each gamont is present in a parasitophorous vacuole cytoplasm is filled with dense granules. Destruction of the host cell can be noticed. 5. Photomicrograph of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata showing two macrogamonts. Note: large nucleus with a nucleolus. 6. Photomicrograph of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata showing one microgamont and other macrogamont. Note: Damage of the host cell nucleus. 7. Photomicrograph of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Ciona intestinalis showing two microgamonts. Note: enlarged nucleus of one gamont and damage of the host cell nucleus. 8. Photomicrograph of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Ciona intestinalis showing a multinucleated microgamont inside the paracytophorous vacuole. Note: four nuclei inside the gamont. |
Invaginations or cytostomes were also observed (Fig.21). Cytostomes are sometimes connected with food vacuoles. The amount of amylopectins increased in the zygote stage. The oocyst was surrouned by two homogenous layers, similar to each other in shape and electron dense characteristics. A third layer appeared interiorly irregularly shaped with highly dense electron material (Fig.21). As the oocyst developed, the nucleus became homogenous and provided with a nucleolus and the third layer thickened and cracked. Gradually the parasitophorous vacuole disintegrated followed by complete lysis of the lecocyte host cell. Flattening of the neighbouring cells occurred due to gradual enlargement of the oocyst (Figs.20–21).
Schizogony
First generation schizont
After ingesting the unsporulated sporocyst through the oral opening in both ascidians studied, a process of sporogony occurred in the lumen of the intestine and the sporozoites released and penetrated the intestinal mucosa where the agametic cycle started. The first generation schizont appeared afterwards and schizonts increased in number especially in the lower part of the intestine. Different morphological appearances of the first generation schizont were observed. Each schizont underwent stages of development and another differentiation stage to form sporozoites. Schizonts (17.2 X 15 µm) pushed or overlooked the nucleus of the host intestinal mucosa meanwhile, the cytoplasm of the host cell became very narrow (Fig.22). A number of projections appeared on the outer boundary of the infected host cell and extended in the direction of the other epithelial cells at the vicinity. As their nuclei became branched and lobulated, schizonts underwent a differentatiation process. The lobules of the schizont nucleus began to separate from each other and migrate to the periphery and the host cell, at this time the host cell is totally occupied with the schizont (21.6 X 16 µm). sporozoites with fusiform shape (4.3 X 1.8 µm) released and wandered free in the cytoplasm of the host cell. The rest of sporozoites were still attached to the residual body.
The schizont diameter in this stage was (13.4 X 12.8 µm). The total number of sporozoites in each schizont was more or less 64.
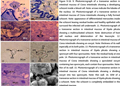 Figure 9-16 9. Photomicrograph of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Ciona intestinalis showing a developing schizont inside a blood cell. Note: arrows indicate the lobules of the nucleus. 10. Photomicrograph of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Ciona intestinalis showing a fully formed schizont. Note: appearance of differentiated merozoites inside the schizont leaving residual bodies and healthy epithelial cells surround the infected cell underneath. 11. Photomicrograph of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata showing a multinucleated schizont. Note: destruction of host cell nucleus and deterioration of the leucocyte. 12. Photomicrograph of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Ciona intestinalis showing an oocyst. Note: thickness of its wall especially at its both poles. 13. Photomicrograph of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata showing a sporocyst with four sporouoites. Note: the residual body at one pole. 14. Photomicrograph of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Ciona intestinalis showing a sporulated oocyst containing two sporocysts, each contain four sporouoites. Note: thin of its wall. 15. Photomicrograph of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Ciona intestinalis showing a dividing oocyst into two sporocysts. Note: thin wall. 16. SEM of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata showing a schizont. Note: the schizont is completely embedded in the intestinal mucosa. |
Second generation schizont
The sporozoites of the first generation schizont now became free of the host infected intestinal epithelia and entered other cells to form schizonts of second generation (Fig. 22). Each with about 43 nuclei (12.3 X 8.5 µm). Schizonts enlaged gradually in diameter (15.2 X 10.3 µm) and had similar morphology and characteristics of the first generation schizont.
So, it can be concluded that schizonts of the first generation were larger in diameter and contained more number of sporozoites compared with the schizonts of the second generation.
Scanning electron microscopy revealed that the sporozoite appeared cylindrical in shape with a rigid pellicle (Fig. 23). Transmission electron microscopy revealed that schizonts of the first generation were completely embedded in the epithelial cells and rested near the basal membranes. projections (37.4 X 29.7 µm) appeared from the host infected intestinal epithelial cells. Schizonts were free in the cytoplasm of the host cell and surrounded with a double membrane pellicle (Figs.24-25). The host epithelial cells in this stage were highly vacuolated and the pellicular invaginations of the schizont took place in the direction of these vacuoles. Sporogony inside the schizont took place after the formation of the conoid, a single unit membrane and subpellicular microtubules (Figs.25-26). Sporozoites after release had a number of vesicles anteriorly which are similar to that seen inside the cytoplasm of the schizont. Perhaps these sporozoites vesicles are precursors of the micronemes (Fig.27).
.png) Figure 17-24 17.TEM of a transverse section of intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata showing a uninucleated trophozoite. 18. TEM of a transverse section of intestinal mucosa of Ciona intestinalis showing a uninucleated trophozoite. Note: appearance of dark granules inside its cytoplasm. 19. TEM of a transverse section of intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata showing an early formed gamont inside the parasitophorous vacuole. Note: disappearance of apical complex. 20. TEM of a transverse section of intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata showing an oocyst during wall formation. Note: large nucleus containg a nucleolus and appearance of cracks in the oocyst wall. 21. TEM of a transverse section of intestinal mucosa of Ciona intestinalis showing an oocyst. Note: oocyst wall has three homogenous layers. 22. SEM of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata showing schizont of second generation. Note: the schizont now became free of the host infected intestinal epithelia. 23. SEM of a transverse section in intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata showing sporozoite of second generation. Note: the sporozoite appeared cylindrical in shape with a rigid pellicle. 24. TEM of a transverse section of intestinal mucosa of Ciona intestinalis showing a scizont. Note: each nucleus is surrounded with a single membrane, a number of merozoites surrounded by dark granules separate from the schizont. |
Dense bodies were observed while movement from the developing schizont cytoplasm to inside the sporozoites. As sporozoites developed, a constriction of nucleus took place and some organelles appeared in the cytoplasm represented by mitochondria, Golgi complex and endoplasmic reticulum (Figs.28-29). A part of the outer layer of the schizont pellicle pinch off from the schizont forming the outer boundary of the sporozoites. At this stage, a number of mitochondria were observed beside the developing merozoites. Ultrastructurally, the sporozoites was surrouded with a double pellicular membrane, provided with subpellicular microtubules, visible endoplasmic reticulum in its cytoplasm, uninucleated, provided with micropores, 2-4 tubular mitochondria, provided with anterior polar ring, provided with a number of micronemes and a multiple membrane bounded vesicle represented by the apicoplast. Sporozoites initiate infection probably when released in the lumen of the gut from an ingested sporulated oocyst or free sporocyst (homoxenous), or from an ingested intermediate host (heteroxenous). Sporozoites then enter host gut epithelial cells, or travel to extraintestinal sites, and there transform into trophozoites which become meronts (Fig.30). These divide by agametic proliferation, merogony, to form merozoites which may enter new host cells extraintestinal to produce more merogonous cycles (Fig.31). Usually, in coccidia, there are fixed numbers of agametic generations. Merozoites of the final merogony enter host cells to initiate the gametic cycle, and become either macrogamonts or microgamonts (Fig.32). The former develop into macrogametes without further division whilst microgamonts divide by multiple fission to produce large numbers of flagellated microgametes. Microgametes fertilize macrogametes to produce zygotes and the cycle will be repeated.
Discussion
Coccidians represent the largest group of organisms within the Apicomplexa and they have a wide range of animal hosts (Levine, 1988; Cox, 1994; Upton, 2000). There are relatively few reports documenting the parasites shed by sea squirts. This study revealed in the investigated coccidian that, the apical complex present at some stages, usually comprising polar ring, rhoptries, micronemes, conoid and subpellicular microtubules. The Conoid usually present and forms a complete cone; reproduction usually agametic in the intestinal mucosa and gametic extraintestinally as in blood cells. Oocysts contain infective sporozoites which result from sporogony; locomotion was by flagella. Gamonts are usually present, small and intracellular; conoid not modified into mucron or epimerite; syzygy involved gametes; anisogamy; life cycle characteristically involves merogony, gamogony and sporogony.
Oocysts had two sporocysts, each with four sporozoites; sporocysts are univalved, without dehiscence line; sporogony, merogony and gamogony within host cell. The present study concluded that the investigated parasite may belong to Genus Isospora (Schneider, 1881) since isosporans sporogony contrasts with that of eimerians where sporulatuation is endogenously (McConnell, Vos, Basson and De Vos, 1971). Long and Joyner (1984) discussed the problem of identification of species of coccidians, and they indicated the limitations of using morphological data derived from oocysts and the necessity for using other characteristics. However, the oocyst and, in particular the structure of its contained sporocysts, are considered important features in differentiating genera and species. This study concluded that development of the present coccidian is endogenous and follows a eucoccidian pattern of merogony, gamogony and sporogony. Similar results of the present study were found describing the general morphology of the uninucleated zoite (Paterson and Desser, 1981a&b; Molnir and Baska, 1986). The early trophozoite (derived from the sporozoite) is usually rounded. That of Goussia iroguoina contains remnants of micronemes, mitochondria, and a nucleus with a prominent nucleolus, and lies within a parasitophorous vacuole (Paterson and Desser, 1981c&d). The youngest trophozoites of Epieimeria anguillae are surrounded by two unit membranes (Molnir and Baska, 1986). Later trophozoites of Goussia iroguoina derived from merozoites of the previous generation, usually contain the remnants of the pellicular complex, micronemes, a nucleus with a prominent nucleolus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum and vesicles (Paterson and Desser, 1982). Before merogony, the trophozoite may roundup, loses its pellicle and undergoes nuclear division. The present study revealed that sporogony took place in the intestinal epithelium whereas merogony and gamogony were in the circulatory system and this conclusion contradicts that of Davies, (1978); Hawkins et al., (1984); Molnar et al., (2005). The site of merogony may be the same as that in which gamonts, oocysts, and early sporogony occur. This is true of Eimeria variabilis, Calyptospora funduli and Eimeria (Davies, 1978; Hawkins et al., 1984; Molnar et al., 2005). Sometimes, however, its location is very different from the site of gamonts or subsequent stages. In Eimeria brevoortia, for example, merozoites and gamonts apparently occur in the intestine, while sporogony occurs in the swim bladder (Hardcastle, 1944). In several instances the study of experimentally infected hosts has done much to improve understanding of the sequential agametic development of coccidians. Merogony in several fish coccidians is similar to that seen in homeotherm hosts. Meronts of Goussiu iroquoina, Goussia sinensis, and Goussiu carpelli develop within parasitophorous vacuoles (Paterson and Desser, 1981d; Baska and Molnar, 1989; Steinhagen, 1991; Molnar et al., 2005), but no parasitophorous vacuole was evident surrounding two meronts of Eimeria variabilis (Davies, 1990). In most coccidians the parasitophorous vacuole membrane is produced by the host cell, but its origin varies. The host cell plasmalemma often forms the vacuole membrane during the process of phagocytic entry by the sporozoite or the merozoite of the previous generation. Merozoites appear to be produced by three methods: exogenesis (ectomerogony), in which merozoites are budded from the surface of the meront; endomerogony, in which several merozoites are produced within the meront; and endodyogeny, in which paired merozoites are produced internally. The ultrastructure of merozoites of piscine coccidians resembles that of other closely related coccidians (Scholtyseck, 1973; Chobotar and Scholtyseck, 1982; Ball and Pittilo, 1990). Merozoites of Eimeriu vunusi are bound by two unit membranes (Paperna, 1990); those of Goussiu sinensis are bound by a three-layered pellicle (Baska and Molnar, 1989). Young macrogamonts are usually 5.0-26.0 pm in diameter. They are mostly spherical or ellipsoidal structures surrounded by one or more delicate membranes and they commonly lie within a parasitophorous vacuole. Young macrogamonts of Goussia iroquoina have elaborately shaped mitochondria, granular endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi complexes (Paterson and Desser, 1981a). Microgametogenesis of the present study follows a basic pattern similar to that described for coccidians. A phase of nuclear division associated with growth of the microgamont preceded differentiation of microgametes (Scholtyseck, 1973: Chobotar and Scholtyseck, 1982; Ball and Pittilo, 1990). Coccidians that have been shown to conform to this pattern of development include, for example, Goussia iroquoina, Goussia aculeati, and Goussia zarnowskii (Paterson and Desser, 1981b; Jastrzebski, 1989; Jastrzebski and Komorowski, 1990). This observation contradicted to that of Eimeria vanusi, in which the microgamont nucleus does not subdivide before microgamete formation (Paperna, 1990). Microgamonts develop within a parasitophorous vacuole, which in Goussia iroquoina, Calyptospora funduli and Goussia sinensis is bound by a single limiting membrane (Hawkins et al., 1983; Paterson and Desser, 1984; Baska and Molnar, 1989). Oocysts tend to be spherical or ellipsoid structures (generally 4.5-70 pm in diameter, depending on species), although some are cylindrical, as those of Eimeria southwelli Halawani, 1930 and Eimeria quentini Boulard, 1977. The oocyst walls are commonly thin, and one species, Goussia sinensis, is reported to have a micropyle (Chen, 1956). Some thin oocyst walls tend to collapse on to the sporocysts following sporulation. In coccidians of homeotherms the oocyst wall tends to be thick, and is formed from two types of wall-forming bodies (WF1 and WF2) that are discharged around the fertilized macrogamete, but in fish coccidians these bodies are not always recognized. Bodies resembling the wall-forming bodies of coccidians of homeotherms have been described, but some of these may be involved in sporocyst wall formation. Oocysts vary in their site of development. As for other stages of fish coccidians, the gut is a favoured location but extraintestinal sites where oocysts may be found include liver, kidney, spleen, pancreas, testes, ovary, peritoneum, swim bladder, gall bladder, adipose tissue and gill filaments. Within the same species, oocysts may occur in the same location as merozoites and gamonts, or at different sites, suggesting that in some cases migration occurs. Sporocyst walls of Goussia auxidis were found to consist of three layers. The outer layer was a laminar envelope with 2-12 laminations parallel to the wall, an electron dense layer 14 nm thick, and a transversely laminated wall 160-180 nm thick. Dispersal of oocysts from the gut of fish occurs presumably in the faeces, where oocysts may be passed unsporulated, semisporulated, or fully sporulated. Tissue-inhabiting coccidia such as Eimeriu sardinae from the testes of a number of fish coccidia apparently undergo “migration” during development, but there is little to indicate how this occurs.
Sporozoites initiate infection probably when released in the lumen of the gut from an ingested sporulated oocyst or free sporocyst (homoxenous), or from an ingested intermediate host (heteroxenous). Sporozoites then enter host gut epithelial cells, or travel to extraintestinal sites, and there transform into trophozoites which become meronts. These divide by agametic proliferation, merogony, to form merozoites which may enter new host cells extraintestinal to produce more merogonous cycles. Usually, in coccidia, there are fixed numbers of agametic generations. Merozoites of the final merogony enter host cells to initiate the gametic cycle, and become either macrogamonts or microgamonts. The former develop into macrogametes without further division whilst microgamonts divide by multiple fission to produce large numbers of flagellated microgametes. Microgametes fertilize macrogametes to produce zygotes and the cycle will be repeated.
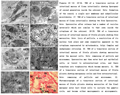 Figure 25-32 25-26. TEM of a transverse section of intestinal mucosa of Ciona intestinalis showing Sporogony of second generation inside the schizont. Note: formation of the conoid, a single unit membrane and subpellicular microtubules. 27. TEM of a transverse section of intestinal mucosa of Ciona intestinalis showing two free Sporozoites. Note: Sporozoites after release had a number of vesicles anteriorly which are similar to that seen inside the cytoplasm of the schizont. 28-29. TEM of a transverse section of intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata showing free merozoites. Note: lysis of pellicle, a constriction of its nucleus took place and some organelles appeared in the cytoplasm represented by mitochondria, Golgi Complex and endoplasmic reticulum. 30. TEM of a transverse section of intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata showing merozoites enter the mucosal cells. Note: remaining of pellicle and micronemes. Sporozoites may then enter host gut epithelial cells, or travel to extraintestinal sites, and there transform into trophozoites which become meronts. 31. TEM of a transverse section of intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata showing merogonous cycles and free extraintestinal. Note: remaining of pellicle and micronemes. 32. Photomicrograph of a transverse section of intestinal mucosa of Styela plicata showing merozoites of the final merogony enter host blood cells to initiate the gametic cycle, and become either macrogamonts or microgamonts. Note: remaining of pellicle and micronemes. |
Abbreviations
|
A |
Amylopectin |
|
AS |
Atrial Siphon |
|
C |
Conoid |
|
BC |
Blood Cell of The Host |
|
DG |
Dense Granules |
|
DM |
Differentiated merozoites |
|
DO |
Remains of Dense granules |
|
EC |
Epithelial Cell (surround the infected cell) |
|
EL |
Epithelial layer |
|
ER |
Endoplasmic Reticulum |
|
FM |
Free Merozoite |
|
G |
Gamont |
|
HC |
Host Cell |
|
HCN |
Host Cell Nucleus |
|
IVM |
Primary Vacuole Membrane |
|
LA |
Leucocytes |
|
M |
Merozoite |
|
MAG |
Macrogamont |
|
MI |
Mitochondria |
|
MIG |
Microgamete |
|
MN |
Micronemes |
|
MP |
Micropyle |
|
MPV |
Membrane of Parasitophorous Vacuole |
|
N |
Nucleus |
|
NU |
Nucleolus |
|
OC |
Oocyst |
|
OCW |
Oocyst Wall |
|
OS |
Oral Siphon |
|
PE |
Pellicle |
|
PV |
Parasitophorous Vacuole |
|
RB |
Residual Body |
|
SCH |
Schizont |
|
SPC |
Sporocyst |
|
SPR |
sporozoites |
|
SRB |
Sporocyst Residual Body |
|
SW |
Sporocyst Wall |
|
T |
Tunic |
|
V |
Vacuole |
|
VE |
Vesicle |
|
ZU |
Uninucleated Zoite |
|
WL2 |
Second Wall of Oocyst |
|
WL3 |
Third Wall of Oocyst |
Ball S. J., and Pittilo R. M., 1990, Structure and ultrastructure. In Long, P. L. ed. “Coccidiosis of Man and Domestic Animals”. pp. 17- 41. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Baska F., and Molnar K., 1989, Ultrastructural observations on different developmental stages of Goussiu sinensis (Chen, 1955), a parasite of the silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix Valenciennes, 1844). Acta Veterinaria Hungarica, 37, 81-87.
Boulard Y., 1977, Description d'Eimeria quentini n. sp., parasite intranucleaire du peritoine de la raie: Aetobatis narinari (Chondrichthyens, Myliohatidae) en Malaisie. Protistologica, 13, 529- 533.
Buchmann K., and Lindenstrøm T., 2002, Interactions between monogenean parasites and their fish hosts. Int. J. Parasit., 32:309-319.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7519(01)00332-0
Campbell, R. A., Haedrich R. L, and Munroe T. A., 1980, Parasitism and ecological relationships among deep-sea benthic fishes. Marine Biol., 57:301-313.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF00387573
Chen H. C., 1956, The protozoan parasites from four species of Chinese pond fishes: Ctenopharygodon idellus, Mylopharyngodon piceus, Aristichthys nobilis and Hypophthalmichthys molithrix. III. The protozoan parasites of Aristichthys nobilis and Hypophthalmichthys molithrix. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, No. 2, 279-298.
Chobotar B., and Scholtyseck E., 1982, Ultrastructure. In “The Biology of the Coccidia” (P. L. Long, ed.), pp. 101-165. University Park Press, Baltimore.
Ciancio A. , Scippa S., and Izzo C., 1999, Ultrastructure of vegetative and sporulation stages of Hapiosporidium ascidiarum from the ascidian Ciona intestinaiis L. Europ. J. Protistol. 35, 175-182.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0932-4739(99)80035-2
Cox F. E. G., 1994, The evolutionary expansion of the Sporozoa. Inter. J. Parasit., 24: 1301–1316.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0020-7519(94)90197-X
Davies A. J., 1978, Coccidian parasites of intertidal fishes from Wales: systematics, development and cytochemistry. J. Protozool., 25, 15-2 1
Davies A. J., 1990, Ultrastructural studies on the endogenous stages of Eimeria variabilis (Thelohan, 1893) Reichenow 1921, from Cottus (Taurulus) bubulis Euphrasen (Teleostei: Cottidae). J. Fish Diseases, 13, 447461.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.1990.tb00804.x
Diouf J. N., and Toguebaye B. S., 2013, An ultrastructural study on the merogonic stages of Goussia senegalensis (Faye, 1988) Diouf and Toguebaye, 1993 (Apicomplexa, Coccidia) from the liver of Pagellus bellottii (Pisces, Teleostei). Turkish J. Zool., 37: 643-646.
http://dx.doi.org/10.3906/zoo-1207-32
Duszynski D.W., Bolek M. G., and Upton S. J., 2007 Coccidia (Apicomplex: Eimeriidae) of amphibians of the world. Zootaxa.,1667: 3-77.
George-Nascimento M. A., 1987, Ecological helminthology of wildlife animal hosts from South America; a literature review and a search for patterns in marine food webs. Revista Chilena de Historia Natural., 60:181-202.
Hardcastle A. B., 1944, Eimeria brevoortiana, a new sporozoan parasite from the menhaden (Brevoortia tyrannus), with observations on its life history. J. Parasit., 30: 60-68.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3272569
Hawkins W. E. , Solangi M. A., and Overstreet R. M., 1983, Ultrastructure of the macrogamont of Eimeria funduli, a coccidium parasitizing killifishes. J. Fish Diseases, 6: 33-43.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.1983.tb00049.x
Hawkins W. E. , Fournie J. W., and Overstreet R. M., 1984, Ultrastructure of the interface between stages of Eimeria funduli (Apicomplexa) and hepatocytes of the longnose killifish, Fundulus similis. J. Parasit., 70: 232-238.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3281868
Hoberg E. P., 1996, Faunal diversity among avian parasite assemblages:nthe interaction of history, ecology and biogeography in marine systems. Bull. Scandinavian Soc. Parasitol., 6: 65–89.
Huxam M. , Raffaelli D., and Pike A., 1995, Parasites and food web patterns. J. Animal Ecol., 64:168-176.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/5752
Jastrzebski M. 1989, Ultrastructural study on the development of Goussia aculeati, a coccidium parasitizing the three-spined stickleback Gasterosteus aculeatus. Dis. Aquat. Org., 6: 45-53.
http://dx.doi.org/10.3354/dao006045
Jastrzebski M., and Komorowski Z., 1990, Light and electron .microscopic studies on Goussia zarnowskii (Jastrzebski, 1982): an intestinal coccidium parasitizing the three-spined stickleback, Gasterosteus aculeatus (L.). J. Fish Diseases, 13: 1-24.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.1990.tb00753.x
Jirku M., Modry D. , Slapeta J. R., Koudela B., and Lukes J., 2002, The phylogenyof Goussia and Choleoeimeria (Apicomplexa; Eimeriorina) and the evolution of excystation structures in coccidia. Protist., 153: 379-390.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1078/14344610260450118
Jirku M., and Modry D., 2006, Extra-intestinal localization of Goussia sp. (Apicomplexa) oocysts in Rana dalmatina (Anura: Ranidae), and the fate of infection after metamorphosis. Dis. Aquat. Org., 70: 237-241.
http://dx.doi.org/10.3354/dao070237
Khan R. A., and Thulin J., 1991, Influence of pollution on parasites of aquatic animals. Advances in Parasit., 30:204-238.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0065-308X(08)60309-7
Knudsen R. , Amundsen, A. , Jobling M., and Klemetsen A., 2009,Differences in pyloric caeca morphology between Arctic char Salvelinus alpines ecotypes: adaptation to trophic specialization or parasite-induced phenotypic modifications? J. Fish Biol., 73:275-287.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2008.01934.x
Knudsen R. , Curtis M. A., and Kristoffersen R., 2004, Aggregation of helminthes: the role of feeding behavior of fish hosts. J. Parasitol., 90:1-7.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1645/GE-3184
Lafferty K. D., and Kuris A. M., 1999, How environmental stress affects the impacts of parasites. Limnology and Oceanography, 44: 925-931.
http://dx.doi.org/10.4319/lo.1999.44.3_part_2.0925
Landsberg J. H., and Paperna I., 1987, Intestinal infections by Eimeria (s.1.) vanasi n.sp. (Eimeriidae, Apicomplexa, Protozoa) in cichlid fish. Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et ComparPe, 62:283-293.
Levine N. D., 1988, The protozoan phylum Apicomplexa, 2 volumes.CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, Pp 240.
Long P. L,. and Joyner L. P., 1984, Problems in the identification of species of Eimeria. J. Protozool., 31: 535-541.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb05498.x
MacKenzie K. , Williams H. H. , Williams B. , McVicar A. H., and Siddall R., 1995, Parasites as indicators of water quality and the potential use of helminth transmission in marine pollution studies. Advances in Parasitol., 35:85-144.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0065-308X(08)60070-6
Marcogliese D. J., and Cone D. K., 1997, Parasite communities as indicators of ecosystem stress. Parassitologia, 39:227-232.
Marcogliese, D. J. (2004): Parasites: small players with crucial roles in the ecological theatre. EcoHealth, 1:151-164.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10393-004-0028-3
Marcogliese D. J., 2005, Parasites of the superorganism: Are they indicators of ecosystem health? Inter. J. Parasitol., 35:705-716.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2005.01.015
McConnell E. E. , Vos A. , De Basson P. A., and Vos V., 1971, Isospora papionis n.sp. (Eimeriidae) of the chacma baboon Papio ursinus (Ken 1792). J. Protozool., 18, 28-32.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1971.tb03275.x
Molnar K., and Baska F., 1986, Light and electron microscopic studies on Epieimeria anguillae (Leger and Hollande, 1922), a coccidium parasitizing the European eel, Anguilla anguilla L. J. Fish Diseases, 9: 99-1 10.
Molnar K. , Ostoros G., and Baska F., 2005, Cross-infection experiments Confirm the host specificity of Goussia spp (Eimeriidae: Apicomplexa) parasitizing cyprinidfish. Acta Protozool., 44: 43-49.
Overstreet R. M., 1981,Species of Eimeria in nonepithelial sites. J. Protozool., 28: 258-260.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1981.tb02846.x
Overstreet R. M. , Hawkins W. E., and Fournie J. W., 1984, The coccidian genus Calyptospora n.g. and family Calyptosporidae n. fam. (Apicomplexa), with members infecting primarily fishes. J. Protozool., 31: 332-339.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb02972.x
Overstreet R. M., 1993, Parasitic diseases of fishes and their relationship with toxicants and other environmental factors. Pp. 111-156, in: Couch, J.A., and J. W. Fournie (eds.). Pathobiology of Marine and Estuarine Organisms, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Overstreet R. M., 1997, Parasitological data as monitors of environmental health. Parassitologia, 39:169-175.
Pantin G. F. A., 1948, Notes on microscopical technique for zoologists. Cambridge university press.
Paperna I. 1990, Fine structure of the gamonts of Eimeria (s.1.) vanasi, a coccidian from the intestine of cichlid fishes. Dis. Aquat. Org., 9:163-170.
http://dx.doi.org/10.3354/dao009163
Pascual S., Gonzales A. , Araias C., and Guerra A., 1996, Biotic relationships of Illex condetii and Todaropsis eblanae (Cephalapoda, Ommastrephidae) in the Northeast Atlantic: evidence from parasites. Sarsia, 81:265-274.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00364827.1996.10413624
Paterson W. B., and Desser S. S., 1981a, Ultrastructure of macrogametogenesis, macrogametes and young oocysts of Eimeria iroquoina Molnar and Fernando, 1974 in experimentally infected fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas, Cyprinidae).J. Parasitol., 67: 496-504.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3280480
Paterson W. B., and Desser S. S., 1981b, An ultrastructural study of microgametogenesis and the microgamete in Eimeria iroquoina Molnar and Fernando, 1974, in experimentally infected fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas, Cyprinidae). J. Parasitol., 67: 314- 324.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3280550
Paterson W. B., and Desser S. S., 1981c, An ultrastructural study of Eimeria iroquoina Molnar and Fernando, 1974. in experimentally infected fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas, Cyprinidae). 3. Merogony. J. Parasitol., 28. 302-308.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3280550
Paterson W. B. ,and Desser S . S., 1981d, Rhabdospora thelohani Laguesse, 1906 is not a member of the Apicomplexa. J. Parasitol., 67, 741-744.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3280461
Paterson W. B., and Desser S. S., 1982, The biology of two Eimeria species (Protista: Apicomplexa) in their mutual fish hosts in Ontario.Canadian J. Zool., 60: 764-775.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1139/z82-106
Paterson W., and Desser S. S., 1984, Ultrastructural observations on fertilization and sporulation in Goussia iroquoina (Molnar and Fernando, 1974) in experimentally infected fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas, Cyprinidae). J. Parasitol., 70, 703-7 1 I
Pearse A.G.E., 1968, Histochemistry. Theoritical and applied:Vol. 1. third edition. London. Churchill.
Saad G. A., 2008, Histological and histochemical studies of the process of deutoplasmogenesis (vitellogenesis) in the oocyte of Styela plicata Lesuaer,1823), Styela partita (Stimpson, 1852) and Ciona intestinalis (Linnaeus, 1767). Urochordata- Ascidiacea. Int. J. Aquatic Res., 34(2): 387-411.
Saad G. A., 2010, Light and electron microscopical studies on the development of the neural complex of Ascidia mentula (Urochordata - Ascidiacea). Int. J. Aquatic Res., 36(1), 133-146.
Scholtyseck E., 1973, Ultrastructure. In “The Coccida: Eimeria, Isospora, Toxoplasma and Related Genera” (D. M. Hammond and P. L. Long, eds), pp. 81-144. University Park Press, Baltimore and Butterworths, London.
Scippa S., Ciancio A., and De vincentiis M., 2000, Observations on an Apicomplexan microparasite from the Pericardic Body of Ciona intestinalis L. (Protochordata)'. Europ. J. Protisto., 36, 85-88
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0932-4739(00)80024-3
Steinhagen D., 1991, Ultrastructural observations on merogonic and gamogonic stages of Goussia carpelli (Apicomplexa, Coccidia) inexperimentally infected common carp Cyprinus carpio. European J. Protistol., 27, 71-78.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0932-4739(11)80429-3
Upton S. J., 2000, Suborder Eimeriorina Leger,1911. InLee JJ, Lee dale GF, Bradbury P(eds) An Illustrated Guide to the Protozoa. 2nd edition. Society of Protozoologists, Lawrence, Pp 318-339
. PDF(707KB)
. FPDF(win)
. HTML
. Online fPDF
Associated material
. Readers' comments
Other articles by authors
. Gaber Ahmed Saad
Related articles
. Ascidians
. Filter feedin
. Homoxenous or heteroxenous infection
. Uninucleated zoite
. Sporozoites
. Merozoites
Tools
. Email to a friend
. Post a comment


